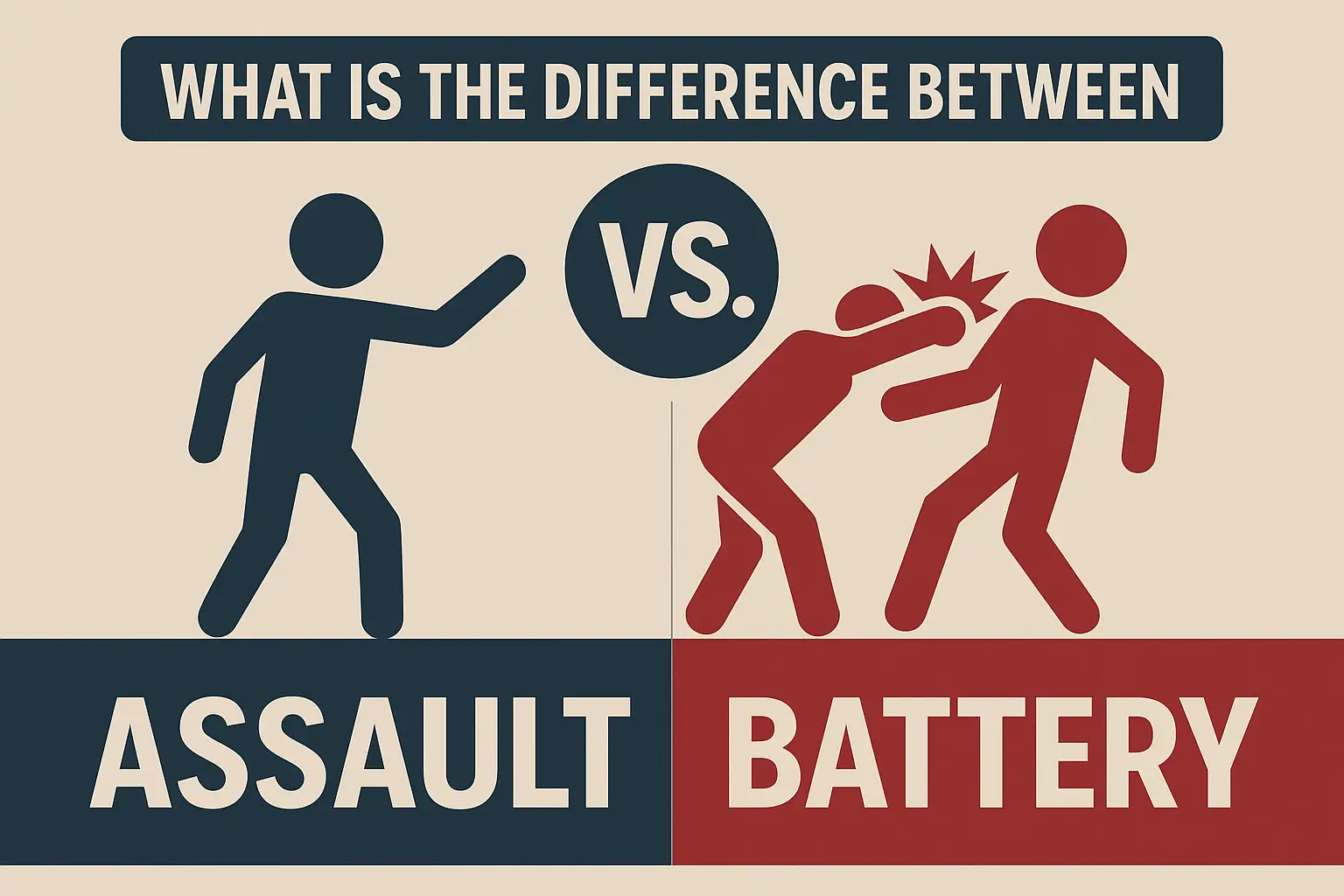
Have you ever wondered what sets assault apart from battery? These two terms often get tangled up, leaving many confused about their true meanings.
Understanding the difference is crucial, especially if you want to protect your rights or the rights of someone you care about. Picture yourself in a situation where every detail counts, and knowing these distinctions could make all the difference. You’re about to uncover the key details that separate these terms, giving you clarity and confidence.
Stick around, because this knowledge could empower you and change the way you view these legal terms forever.

Assault: Legal Definition
Assault involves threatening to harm someone, while battery means actually harming them. Assault doesn’t need physical contact; battery does. Understanding these differences helps in recognizing legal definitions and implications.
Assault is a term often thrown around in everyday conversations, but its legal definition might surprise you. When you hear about assault, you might picture a physical altercation. However, legally speaking, assault doesn’t always involve physical contact. It’s about the threat or attempt to inflict harm. Understanding assault can help you navigate situations where words or actions cross the line into illegal territory.Elements Of Assault
The legal definition of assault hinges on specific elements that must be present. First, there needs to be an intentional act. This means the perpetrator must have deliberately tried to make you fear harm. Second, there must be a reasonable apprehension of imminent harm. If someone threatens you from a distance, you might not feel immediate danger. But if they’re close enough to follow through on their threat, that’s where it becomes assault. Think about a time when someone’s aggressive behavior made you uneasy. Did they have the ability to act on their threats? That fear is a cornerstone of proving assault.Intent In Assault Cases
Intent is crucial in assault cases. It’s not enough to show you were scared; you must prove the person meant to make you feel that way. This involves looking at their actions and words. Did they raise a fist? Did they shout threats? Imagine being at a crowded concert, and someone threatens to punch you because you accidentally bumped into them. If they’re gesturing aggressively, intent might be evident. But if it’s just an angry rant without action, proving intent becomes tricky. Understanding intent can shape how you react in potentially dangerous situations. Knowing someone’s intentions can help you decide whether to seek legal recourse or defuse the situation yourself. As you explore the legal nuances of assault, consider how intent and the elements involved might apply to your experiences. Could you tell the difference between a genuine threat and a meaningless outburst? Recognizing these distinctions can empower you to protect yourself legally.Battery: Legal Definition
Battery is a term often misunderstood by many. It refers to the unlawful physical contact. This contact does not have to cause injury. It simply must be intentional and offensive.
Battery is different from assault. Assault involves the threat of harm. Battery involves actual contact. Understanding the legal definition helps distinguish these terms.
Elements Of Battery
Battery has specific elements that define it. First, there must be contact. This contact must be intentional. It cannot be accidental or negligent.
The contact must be harmful or offensive. Harmful contact causes injury or pain. Offensive contact violates personal space. Both types can result in a battery charge.
Intent In Battery Cases
Intent plays a crucial role in battery cases. The person must intend to make contact. This intent differentiates battery from other acts.
Intent does not mean intent to harm. It means intent to touch or contact. Even if harm was not intended, it can still be battery.
Understanding intent clarifies many legal misunderstandings. It helps in distinguishing between accidental and intentional acts.
Key Differences
Understanding the difference between assault and battery is essential. Both are criminal offenses but have distinct elements. Knowing these can help in legal situations. Let’s explore the key differences under two main aspects.
Intent And Contact
Assault involves the threat of harm. It does not require physical contact. The intent is to create fear of harm. Battery, on the other hand, requires actual physical contact. The intent is to cause harm or offense. Both require intent but differ in execution.
Potential Harm
Assault may not result in physical injury. The harm is psychological, causing fear or apprehension. Battery involves physical harm or offensive contact. The harm can be visible injuries. Both can be serious, but the nature of harm differs.

Examples In Law
Assault involves threatening someone with harm, creating fear, while battery refers to actual physical contact causing injury. Both are serious offenses but differ in nature and legal implications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for recognizing legal responsibilities and rights.
Understanding the distinction between assault and battery can feel like navigating a legal maze. Yet, clear examples from real-life cases can illuminate these differences. By examining actual legal scenarios, you can grasp how these terms play out in courtrooms, which may even challenge what you thought you knew. Dive into these case studies and ask yourself: How do these laws apply to situations you might encounter?Case Studies Of Assault
Consider a scenario where someone raises their fist as if to punch you but stops short of making contact. This action can qualify as assault. The key factor is the intent to instill fear or apprehension of imminent harm. In a famous case, a person verbally threatened another, causing the victim to fear immediate physical harm. Despite the lack of physical contact, the court ruled it as assault. This case highlights that the perception of threat is crucial. Imagine walking down the street and a stranger suddenly lunges at you with an intimidating gesture. Even without physical touch, the fear induced makes it assault. Do you think this aligns with your understanding of assault?Case Studies Of Battery
Battery, unlike assault, involves actual physical contact. Picture an instance where someone shoves another person, causing them to stumble. The act of pushing constitutes battery as it involves unwanted physical interaction. In a notable legal case, an individual was slapped during an argument. The physical action of slapping led to a battery charge. It demonstrates how any non-consensual touch can escalate to legal consequences. Consider a personal experience where you witnessed a friend being poked repeatedly despite asking to stop. This unwanted touch, though minor, could be a case of battery. Can you think of moments where a seemingly small act crossed the line into battery? Understanding these examples helps you better navigate interactions in your daily life. Reflect on your actions and responses, ensuring they align with legal boundaries. How do these insights reshape your perspective on personal space and conflict resolution?Legal Consequences
Understanding the legal consequences of assault and battery is vital. Both offenses carry serious penalties. Each has unique implications in the legal system. Knowing these distinctions can prevent misunderstandings and legal issues. Let’s explore the differences in penalties for assault and battery.
Penalties For Assault
Assault involves the threat of harm without physical contact. It can lead to fines or imprisonment. The severity depends on the intent and circumstances. Simple assault may result in minor penalties. Aggravated assault carries harsher consequences. It often involves weapons or intent to cause serious injury.
Penalties For Battery
Battery involves actual physical contact or harm. It is more severe than assault. Penalties include jail time and significant fines. The level of injury impacts the severity of the punishment. Minor battery may lead to probation. Felony battery involves more serious consequences. It often includes longer prison sentences.

Defenses In Assault And Battery
Assault involves causing someone to fear harm, while battery involves actual physical contact. Both terms relate to personal harm. Understanding the differences can help in legal defenses against these charges.
Understanding the defenses available in assault and battery cases can be crucial, whether you find yourself in a legal predicament or simply wish to know your rights. Not every altercation leads to a guilty verdict; sometimes, the context or circumstance may justify the actions. Let’s unpack some common defenses and see how they might apply in real-world situations.Self-defense
Self-defense is one of the most common defenses used in assault and battery cases. If you are attacked, the law often permits you to defend yourself, but only with reasonable force. The key is proportionality—your response should match the level of threat you face. Imagine someone lunging at you in a dimly lit parking lot. Reacting by pushing them away might be justified, but escalating to lethal force could land you in more trouble. Always question if your response is necessary and appropriate under the circumstances.Consent And Accidental Harm
Did you know that consenting to an activity can sometimes protect you from assault charges? Think about contact sports like boxing or wrestling. Participants generally can’t claim assault because they consent to the physical contact inherent in the sport. However, this doesn’t give a free pass for all actions. If the contact exceeds what’s typically expected in the activity, consent may no longer apply. Accidental harm also plays a role, as not every injury results from malicious intent. Consider if both parties understood the risks involved, which can sometimes blur the lines between legal responsibility and unfortunate accidents. The defenses in assault and battery cases are as varied as the situations themselves. Would you know which defense fits your scenario? Understanding these nuances can arm you with the knowledge to protect your rights effectively.Assault And Battery In Different Jurisdictions
Understanding the differences between assault and battery is crucial. These terms often confuse people due to their overlapping nature. In various jurisdictions, their definitions can differ significantly. This section explores how assault and battery vary across different legal frameworks worldwide.
Variations In Legal Definitions
Legal definitions of assault and battery can differ. Some jurisdictions define assault as a threat or attempt to harm someone. Others require actual physical contact for assault. Battery usually involves physical contact or harm. But definitions can vary based on local laws.
In some places, assault may include non-physical threats. Battery might involve any unwanted touching. Different states in the U.S. have unique interpretations. This can lead to varied legal outcomes.
International Perspectives
Globally, assault and battery definitions vary greatly. In the UK, assault might refer to threats without contact. Battery involves actual physical harm. Many European countries follow similar patterns.
In Asia, definitions may blend traditional and modern laws. Cultural factors can influence interpretations. In Australia, the law distinguishes between common assault and aggravated assault. These terms can have specific meanings in different regions.
Understanding these variations helps navigate legal systems. It ensures clarity in legal proceedings worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Defines Assault In Legal Terms?
Assault is an intentional act that causes fear of imminent harm. It doesn’t require physical contact but involves a threat. The victim must reasonably perceive the threat as immediate and real.
How Does Battery Differ From Assault?
Battery involves actual physical contact or harm. Unlike assault, battery requires touching or striking the victim. It is an intentional act leading to bodily harm or offensive contact.
Can Assault Occur Without Battery?
Yes, assault can occur without battery. Assault is the threat or attempt to harm, while battery involves actual contact. A person can be charged with assault even if no physical harm occurs.
Is Verbal Threat Considered Assault?
Verbal threats can be considered assault if they create fear of immediate harm. The threat must be perceived as credible and imminent. Mere words may not be enough unless coupled with actions indicating intent.
Conclusion
Understanding assault and battery helps in knowing legal differences. Assault involves threats or attempts to harm. Battery requires physical contact. Both are serious offenses. Knowing these terms ensures better awareness. It helps in legal situations. Protects your rights. Educates on potential consequences.
Knowledge empowers in unexpected scenarios. Stay informed and make wise decisions. Being aware aids in avoiding legal troubles. It also assists in understanding news or legal discussions. Always consult a legal expert for advice. This ensures accurate guidance. Stay safe and informed.

I’m someone who’s always been fascinated by how small differences can lead to big understanding. That’s why I love writing “What’s the difference between…” content; it helps me explore topics from multiple angles and explain them in a clear, practical way. Whether it’s tech, productivity, business, or everyday decisions, I enjoy making complex ideas easier to compare, understand, and act on.